
Network throughput and latency together reflect a network's performance. In a nutshell, network bandwidth refers to the capacity of the network for data to be moved at one time throughput expresses the amount of data and latency refers to the speed at which data is transmitted, as described below. Several related terms - throughput, bandwidth and latency - are sometimes mistakenly interchanged. Throughput also applies to the people and organizations using these systems: Independent of the TPS rating of its help desk software, for example, a help desk has its own throughput rate that includes the time staff spend on developing responses to requests. Databases or other middleware can be discussed in terms of "transactions per second" (TPS) Web servers can be discussed in terms of page-views per minute. Throughput applies at higher levels of the IT infrastructure as well. It can also refer to the number of discrete input or output ( I/O) operations responded to in a second ( IOPS). Likewise, in storage systems, throughput refers to either the amount of data that can be received and written to the storage medium or read from media and returned to the requesting system, typically measured in bytes per second (Bps). In data transmission, network throughput is the amount of data moved successfully from one place to another in a given time period, and typically measured in bits per second ( bps), as in megabits per second ( Mbps) or gigabits per second ( Gbps). A benchmark can be used to measure throughput. Units like "trillion floating-point operations per second (TeraFLOPs or TFLOPS)" provide a metric for comparing the cost of raw computing over time or by manufacturer. More recent measures assume either a more complicated mixture of work or focus on some particular aspect of computer operation.
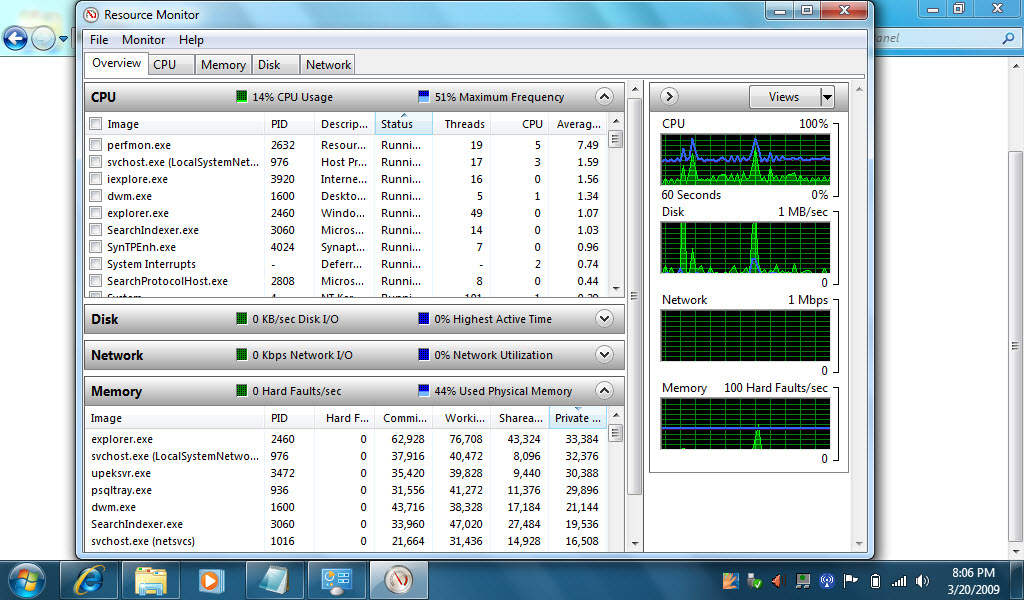
An early throughput measure was the number of batch jobs completed in a day. Historically, throughput has been a measure of the comparative effectiveness of large commercial computers that run many programs concurrently. Related measures of system productivity include the speed with which some specific workload can be completed, and response time, the amount of time between a single interactive user request and receipt of the response. It is applied broadly to systems ranging from various aspects of computer and network systems to organizations. Throughput is a measure of how many units of information a system can process in a given amount of time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
